
Guide to building vs. buying an AI Agent for customer service
This guide will help you assess the build vs buy question from 5 main angles so you can make a confident, informed decision.
Learn More

In the rapidly evolving world of artificial intelligence, we're witnessing remarkable advancements that are reshaping industries and revolutionizing the way we interact with technology.
However, as AI systems become more sophisticated, we're also encountering a fascinating phenomenon known as AI hallucinations. These instances of AI "making things up" are not just quirky anomalies – they represent a significant challenge in the development of reliable and trustworthy AI systems.
AI hallucinations are both a source of frustration and fascination for researchers and practitioners like myself, especially in customer service. They're the AI equivalent of your uncle confidently spouting "facts" at Thanksgiving dinner that turn out to be completely false. Except in this case, the consequences can be far more serious than just an awkward family gathering.
In this post, we'll dive deep into the world of AI hallucinations, exploring real-world examples that illustrate the complexities and potential pitfalls of current AI technologies, with a focus on customer service. We'll examine why these hallucinations occur, their implications for the business, and what's being done to address this challenge.
A hallucination in generative AI occurs when the AI creates information that seems real but isn't accurate or true. This can happen in text, images, or other outputs. While the potential benefits of AI in customer service are significant, the risk of hallucinations can create poor customer experiences if not properly managed.
Understanding the root causes of AI hallucinations is crucial for developing strategies to mitigate them. Here are some of the things happening behind the scenes in the AI that can lead to hallucinations:
Training data quality: AI models trained on datasets containing inaccurate or biased information can reproduce these errors.
Pattern recognition limitations: When faced with queries that don't match clear patterns in their training data, AI models might generate plausible-sounding but incorrect responses.
Model architecture: The underlying design of AI models, focused on pattern recognition and generation, can inherently lead to hallucinations.
Knowledge base and prompt input: Conflicting, ambiguous, or leading information in the input can increase the likelihood of hallucination.
The prevalence of AI hallucinations
The frequency of AI hallucinations can vary significantly depending on the AI system in use. AI hallucinations may happen as infrequently as 3% or as often as 27% of the time, depending on the AI system used. This variability underscores the importance of carefully vetting AI agents and implementing robust prevention and detection mechanisms.
But these statistics are not so disparate from human error. In call centers alone, 66% of agents reported that the primary reason they make mistakes on a call is human error, including forgetfulness, nerves and boredom. Almost o ne-quarter of agents said they forgot the right things to say.
Despite the risk of hallucinations, AI Agents are still automatically resolving up to 70% of customer inquiries. With continuous coaching and management, an AI agent can go above and beyond your expectations.
While we haven’t been able to find a way to completely eliminate hallucinations, we do have practices for prevention, detection, and correction . Before we get into that, let’s take a look at some real examples of when and how AI hallucinates.
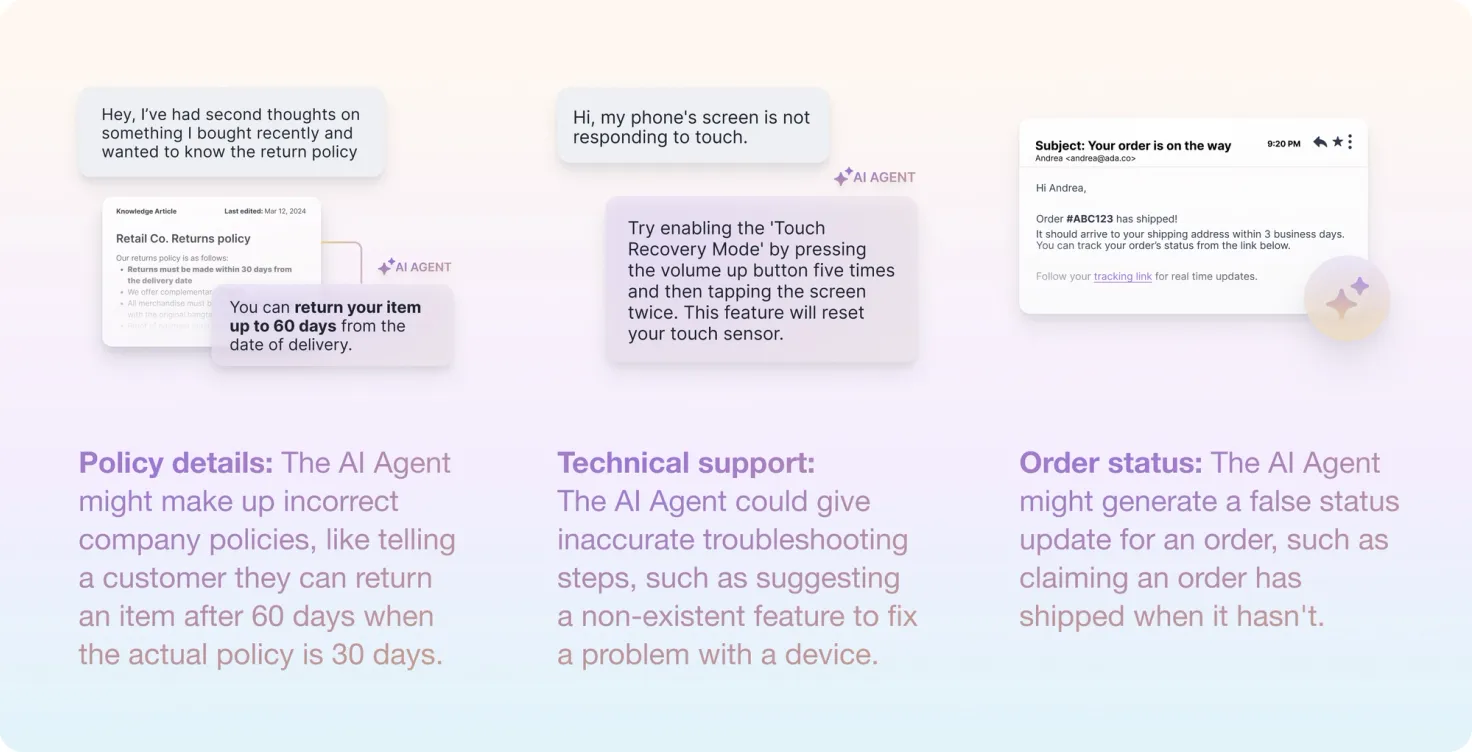
One common area where AI hallucinations occur in customer service is in providing information about company policies. For instance, an AI agent might incorrectly state that a customer can return an item after 60 days when the actual policy is only 30 days. This type of misinformation can lead to customer frustration and potential conflicts when the actual policy is enforced.
For example, in February, Air Canada’s AI-powered chatbot offered a passenger a bereavement discount, stating that if they used it within the next 90 days a portion of his ticket costs would be refunded. But when the passenger went to claim this, Air Canada stated that they don’t offer refunds for travels that have already taken place. It’s a matter of policy. So why did their chatbot serve this false information to a customer?
According to the British Columbia Civil Resolution Tribunal (CRT), Air Canada failed to properly train the AI chatbot with accurate and up-to-date policy information, so in the end, they were ordered to pay the passenger $600 in bereavement refunds, damages, and tribunal costs.
In the realm of technical support, customer service AI agents can sometimes provide inaccurate troubleshooting steps. An AI agent might suggest a non-existent feature to fix a problem with a device. This not only fails to solve the customer's issue but can also lead to confusion and wasted time.
Another area prone to hallucinations is order status updates. An AI agent might generate a false status update for an order, such as claiming an order has shipped when it hasn't. This can cause significant issues in customer expectations and satisfaction.
Is it possible to create an AI agent that never hallucinates? Short answer: We can get close but it’s hard to be perfect. There are ways to mitigate and minimize hallucinations, but current AI technology can’t ensure they never happen — much in the same way that even human agents that are trained experts can make mistakes in their jobs.
That’s why prevention strategies are key. There are several strategies you can employ when managing your AI customer service solution that can significantly reduce the risk hallucinations:
Optimize for Automated Resolutions (AR): Implement AI capabilities that focus on providing relevant, accurate, and safe responses without human intervention.
Even with preventive measures in place, it's crucial to have systems for detecting and correcting hallucinations when they occur. In the same way you have checks with your human customer service agents, your AI agent's work needs a similar review:
AI hallucinations, while challenging, are not insurmountable obstacles for customer service. They're growing pains in the development of a technology that has the potential to revolutionize countless aspects of our lives.
By understanding these hallucinations, developing strategies to mitigate them, and fostering realistic expectations about AI capabilities, we can harness the power of AI while minimizing its risks.
As we continue to push the boundaries of what's possible with AI, let's approach the challenge of hallucinations with a mix of caution and excitement. The journey to create more reliable, trustworthy AI systems is far from over – and that's what makes it so thrilling.
Go deeper. Discover more tips for prevention and get actionable insight on how to quickly identify and correct them.
Get the guide