
Guide to preventing, detecting, and correcting AI Agent hallucinations
Don't let AI hallucinations undermine your customer service. Get the insights you need to keep your AI Agents accurate, reliable and trustworthy.
Learn More

Five years ago, the term Large Language Model (or LLM) would probably be something most people — apart from machine learning scientists and software engineers — would have to Google.
But today, LLMs are at the forefront of AI advancements. We’re seeing their use everywhere, powering a wide range of applications from video and content creation to marketing automation to AI agents for customer service. But we rarely see behind the curtain to learn how companies train large language models for specific applications.
In this post, we’re going to look inside the black box . I spoke with Ada's Manager of Security Operations, Evan Harben, to discover how we, at Ada, use LLM capabilities to impact the customer service strategy, and what training processes we employ to ensure their effective and secure deployment.
Large Language Models are sophisticated AI systems trained on extensive datasets to understand and generate human language. They are integral to generative AI , which focuses on creating new content by learning patterns from existing data.
LLMs are used in various applications, including AI agents, sentiment analysis, text classification, and authorship attribution and authenticity.
Properly training LLMs is crucial to the quality and accuracy of their output. To learn, LLMs process vast amounts of data, in some cases, ingesting over half a trillion parameters to meet expectations of generating coherent and contextually relevant responses.
With proper training, models can understand language nuances and generate accurate responses to even the most complex inquiries. Conversely, inadequate training can lead to hallucinations , misunderstandings, and even security vulnerabilities.
The training process typically involves three key phases:
LLMs enable AI agents to handle inquiries with remarkable speed and accuracy. These models can understand context, provide relevant responses, and even automate complex processes like troubleshooting and personalized recommendations.
This allows businesses to enhance customer satisfaction and allocate human resources to more strategic tasks .
By 2025, AI-driven customer service interactions will increase by 400%.
- Gartner
At Ada, LLMs are integral to the capabilities of our AI Agent. We leverage LLMs to deliver exceptional customer service— and not just for the end user.
We enable businesses to incorporate AI into its core business processes; resolving inquiries with unparalleled efficiency and accuracy allows customer service organizations to transition from an agent-first to AI-first model. Even better, our AI Agent learns from interactions to continually improve its performance.
70% of businesses reported improved customer satisfaction scores after implementing AI-driven customer service platforms.
- McKinsey
But none of this is possible without properly training large language models, most importantly, to protect people’s data privacy and security.
Ada uses state-of-the-art models from providers like OpenAI and Anthropic. We actively evaluate new LLMs as they become available on the market to ensure our platform remains at the cutting edge of AI technology. This includes open source LLM and other LLMs available on the AWS or Azure cloud platforms.
“Our ML teams put tremendous effort into ensuring that Ada’s AI agent provides safe, accurate, and relevant responses. When it comes to model training specifically, each Ada AI agent is trained using information specific to and provided by a single customer, such as those obtained through integrations with a customer Knowledge Base. This approach of grounding the AI’s response in vetted material reduces the risk of the AI giving biased, off-topic, or hallucinated responses.”


Generally, there are two types of data that Ada handles:
This data can exist in two different states:
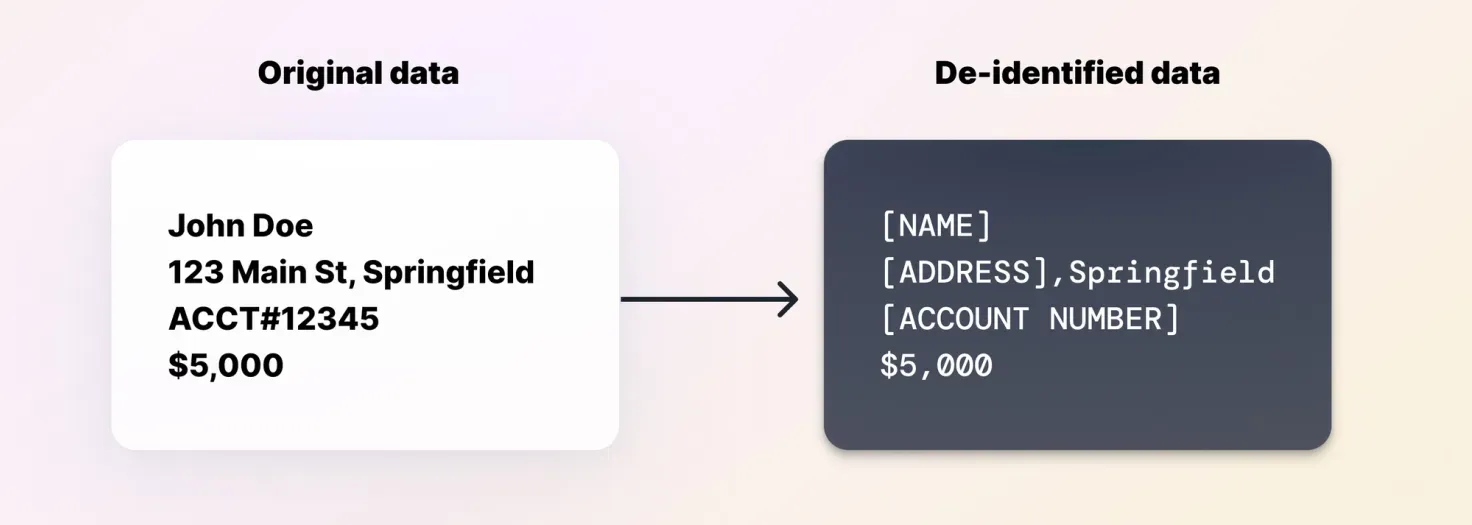
For the most part, Ada uses commercially available LLMs from OpenAI and Anthropic — there’s no personal data or Ada proprietary included in their training. Whenever we do need to fine-tune the LLMs using either end user data, end user metadata, or platform data, it’s always de-identified first, and the customer data used to train the generative models will only serve the specific customer.
“Trust is a foundational part of Ada’s product development and operational practices, and a large part of trust is ensuring that our customer’s data is secure. We ensure alignment with industry standards, regulations, and best practices, and undergo rigorous audits to ensure we’re doing it right. It’s not about just checking a box — it’s about making sure that we’re providing a product and service that our customers can trust.”


Data privacy is a cornerstone of Ada's operations. We align our practices with GDPR guidelines, ensuring that personal data is handled with the utmost care. Our de-identification process leverages advanced technologies to remove sensitive information, such as personally identifiable information (PII) and protected health information (PHI).
We continue to prioritize the privacy and security of our clients' data during the LLM training process. Again, while we use commercially available LLMs, no customer data or proprietary Ada data is involved in their initial training. In cases where fine-tuning is necessary, we use de-identified data specific to each customer, ensuring that personal information is never exposed.
“Among our other practices, Ada employs two key techniques to ensure that customer data is protected when it comes to how it’s used in Generative AI. Zero Data Retention ensures that our LLM providers don’t retain any of the data we pass to them; it is processed, and immediately discarded. Strict enterprise agreements further this protection by prohibiting the use of data we provide to them within their models.”


Our agreements with third-party providers stipulate that any data sent for response generation is not stored long-term or used for training purposes. We adhere to a zero data retention policy, ensuring that our customers' data remains confidential and secure.
As the landscape of AI continues to evolve, the importance of training LLMs effectively is coming into focus. With the right training processes in place, businesses can harness the full potential of AI to enhance customer interactions and drive operational efficiency. It’s a no-brainer.
“There is always going to be a level of risk involved when it comes to using sensitive data within generative AI, no matter which organization or product you go with. At Ada, we’re always looking for ways to reduce that risk as much as possible; we want to make it an easy choice for organizations (particularly their security and compliance teams!) to choose Ada.”


Ada is proud to be at the forefront of this revolution, ensuring that our clients are equipped with the best tools to meet their customers' needs. And as LLMs get smarter, so do we.
As the old adage goes, “It’s not the size of the model, but how you use it.”
Better understand the AI privacy risks and alleviate fear that's holding you back from modernizing your customer service.
Get the guide